Travel Tips
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
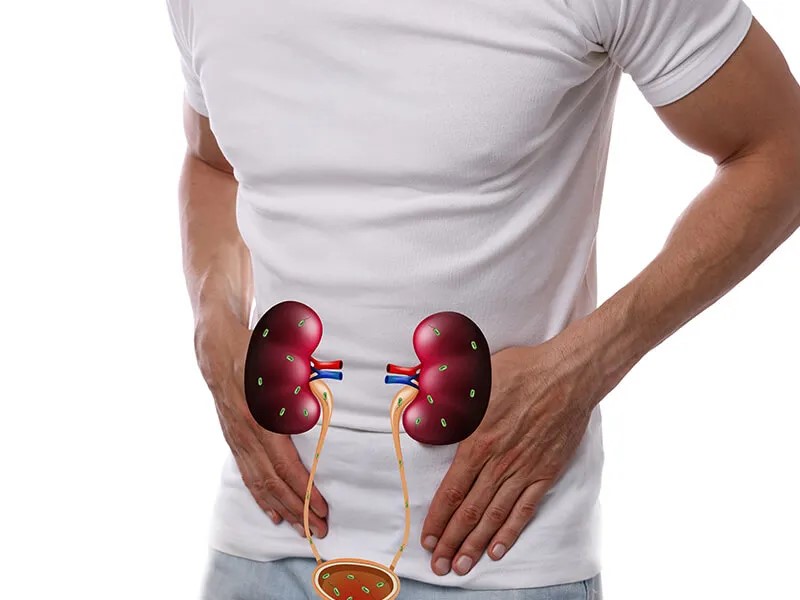
In the biopathic approach to wellness, every organ is seen not just as a physical structure, but as part of the body’s intelligent, self-regulating system. The urinary bladder is a key organ in the elimination system, storing and releasing waste fluids. Though often overlooked, it plays a vital role in maintaining internal purity and body balance.
The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body. It is located in the lower abdomen, behind the pelvic bone.
Capacity: About 400–600 ml of urine in a healthy adult
Shape: Round when full, folded and smaller when empty
Connected Organs: Kidneys (via ureters) and urethra (for elimination)
Urine is formed in the kidneys, passed down to the bladder via the ureters, and expelled through the urethra during urination.
Storage of Urine
The bladder temporarily holds urine, giving the body time to safely eliminate waste.
Controlled Elimination
Thanks to muscular and nerve coordination, the bladder allows voluntary urination at appropriate times.
Detox Support
Through the release of urine, the bladder helps remove toxins, excess minerals, and water, supporting natural detoxification.
Symptoms: Frequent urge to urinate, burning sensation, cloudy urine
Cause: Bacterial infection, often due to poor hygiene, dehydration, or immune weakness
Natural Support: Cranberry juice, D-mannose, neem, coriander water, probiotics
Formed due to concentrated urine or mineral imbalances
Natural Support: Hydration, barley water, gokshura (Tribulus terrestris), and avoiding high-oxalate foods
Sudden urge to urinate frequently, sometimes with leakage
Biopathic Insight: May be linked to stress, nervous system imbalance, or weak pelvic muscles
Natural Remedies: Yoga (especially Moola Bandha), bladder training, pumpkin seeds, magnesium-rich foods
In natural health systems like biopathy, the bladder is seen as a filtering partner of the kidneys, reflecting the body's inner terrain and fluid balance. Keeping it healthy involves supporting the entire urinary system holistically.
Stay Hydrated: Drink clean, filtered water throughout the day.
Eat Alkaline: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and herbs that reduce acidity.
Herbal Support:
Punarnava – for water retention and inflammation
Varuna – supports urinary flow and clears toxins
Shatavari – balances pH and soothes the bladder lining
Pelvic Floor Strengthening: Yoga, squats, and core exercises enhance control and strength.
Emotional Release: In many traditions, bladder issues are linked to unexpressed emotions like fear or anxiety. Journaling, therapy, or meditation can help.
The urinary bladder might seem simple, but it is a powerful detox and balance organ. In biopathy, we honor the bladder as a messenger of the body’s internal cleanliness. By supporting it naturally—through proper hydration, herbs, nutrition, and mind-body harmony—we can maintain a healthy, toxin-free internal environment.
Let your body release what it no longer needs. Nature always knows how to heal.